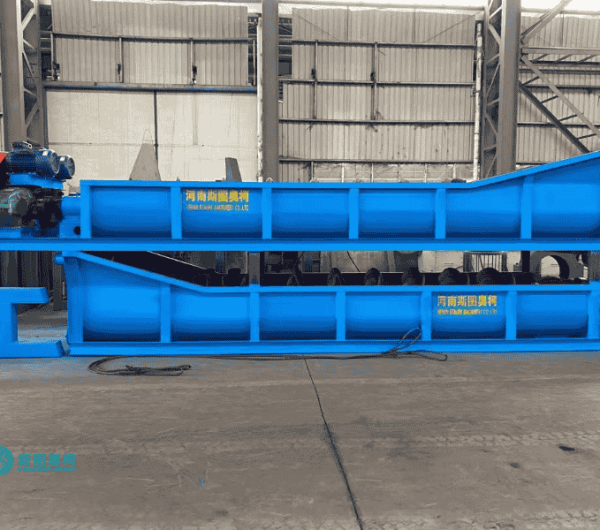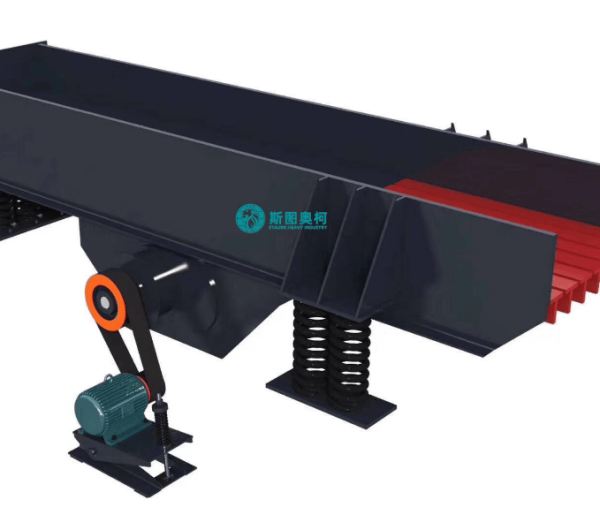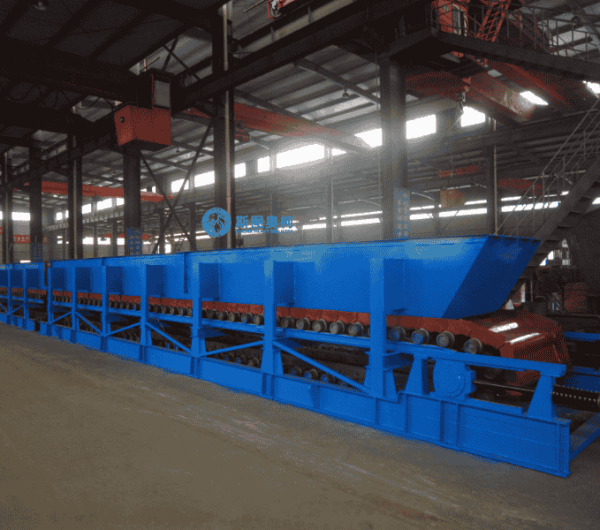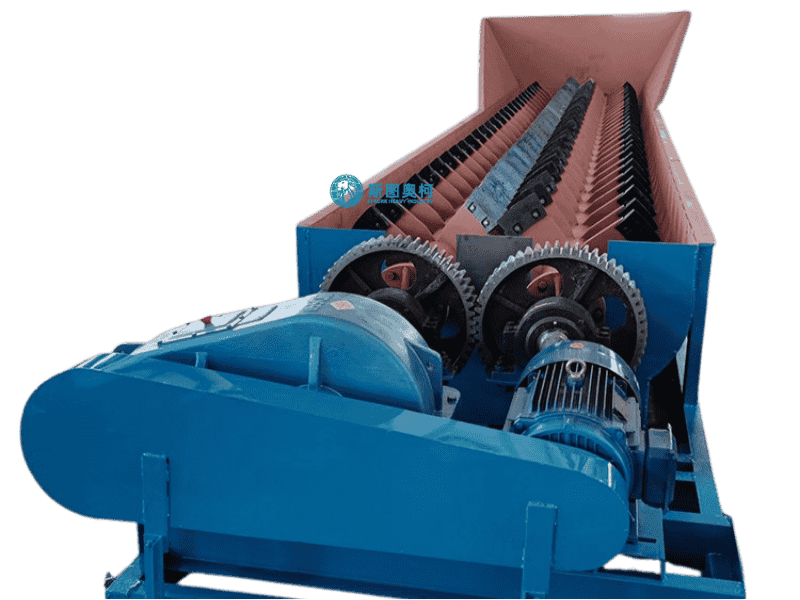
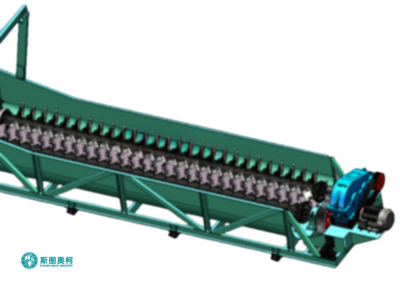
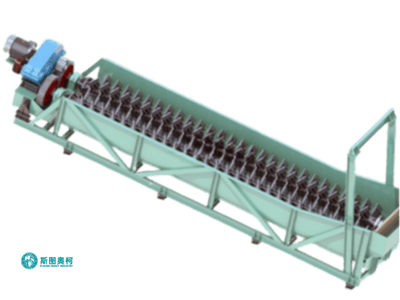
Log Washer
Capacity: 20-400 TPH
Feeding Size: 5-150 mm
Discharging Size: 5-150 mm
Handling Materials: Sand and gravel aggregate, metal ore, etc.
Log washer removes tough clay coatings from 5–150 mm ores/aggregates using rotating shafts with paddles, handling 20–400 t/h. Ideal for high-clay (15–30%) materials like iron ore or demolition waste, it reduces silt content to ≤3% but consumes 3–5 m³/t water.
Advantages
01.
High Clay Removal
Effectively strips 90%+ of sticky clay from 5–150 mm ores via abrasive scouring and high-pressure water jets (0.3–0.5 MPa).
02.
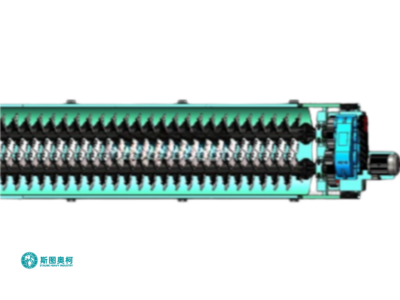
Robust Construction
Wear-resistant alloy paddles and liners withstand abrasive materials (iron ore) for 6,000+ hours of operation.
03.
Large Capacity
Processes 20–400 t/h of gravel or mineral feeds, outperforming manual washing by 10 x in efficiency.

04.
Water Recycling
Integrated slurry discharge allows 80%+ process water recovery when paired with settling ponds.
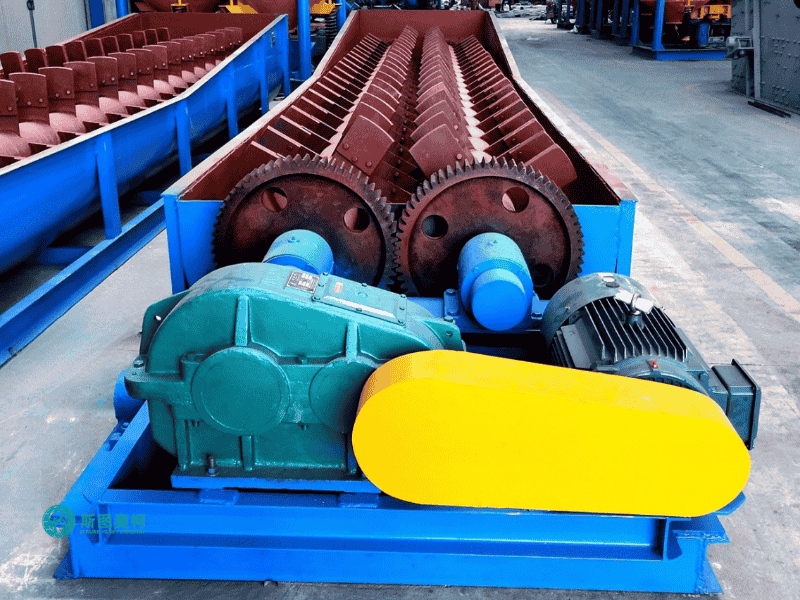
How Does A Log Washer Work
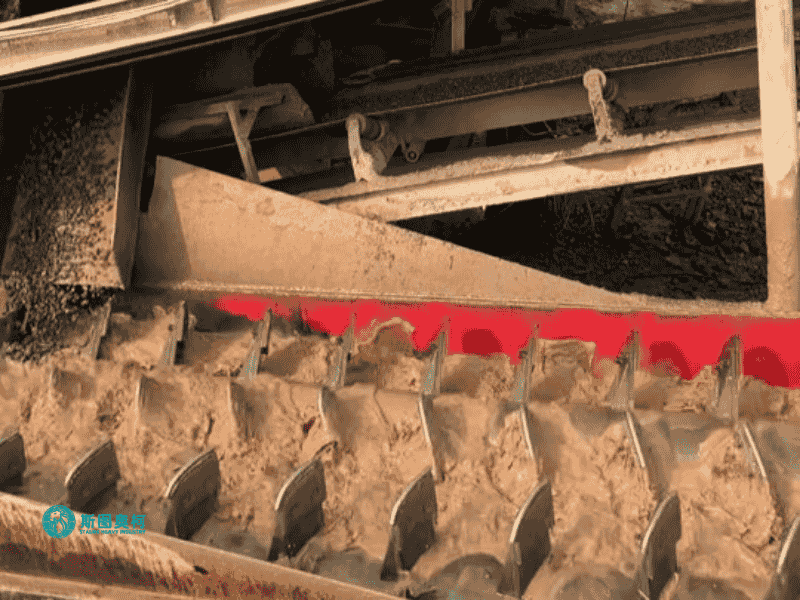
1. Material Feeding: Clay-bound ore (5–150mm) enters the inclined trough, mixed with water to form 20–30% slurry, ensuring optimal scrubbing viscosity.
2. Abrasive Scrubbing: Rotating shafts with welded paddles (10–20 RPM) violently agitate the slurry, forcing particles to collide and dislodge surface clays.
3. Clay Separation: High-pressure water jets (0.3–0.5MPa) flush liberated clays downward as overflow, while cleaned rocks move upward along the trough.
4. Product Discharge: Washed ore exits the elevated end with <3% residual clay; wastewater and fines are channeled to settling systems for recycling.

Applications
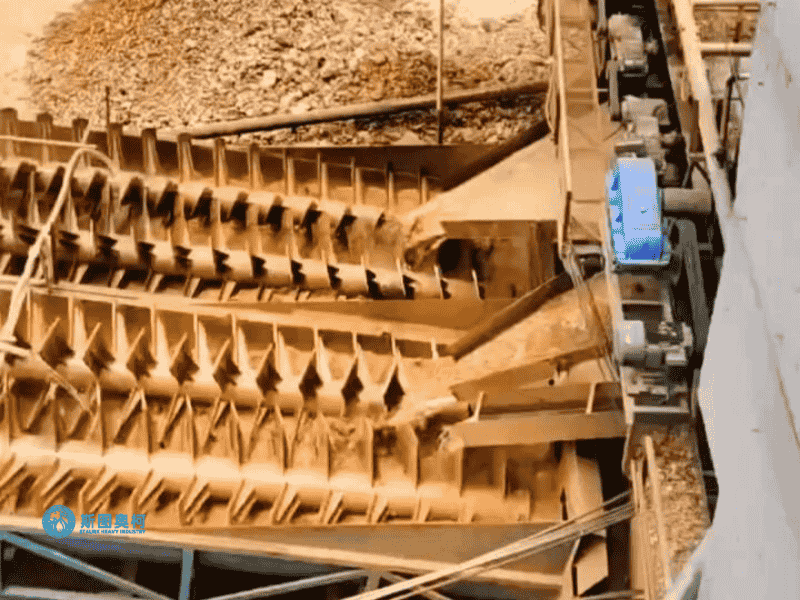
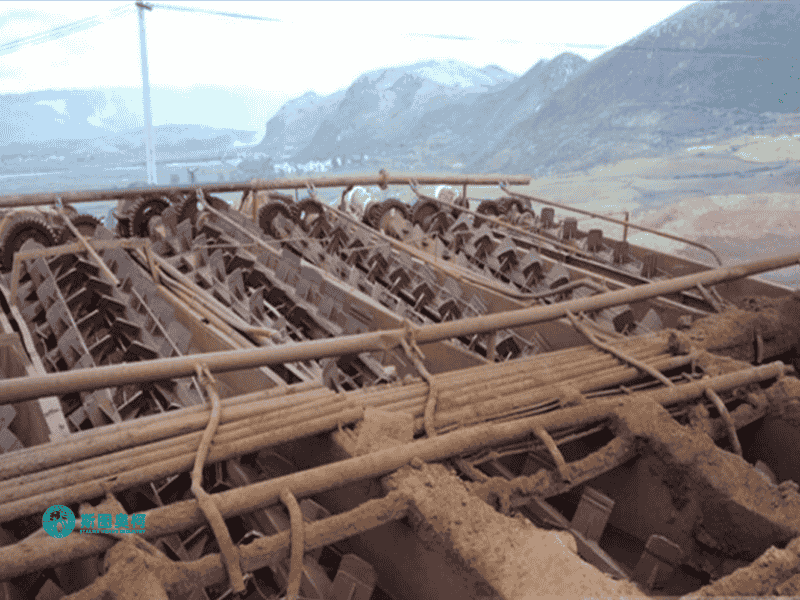
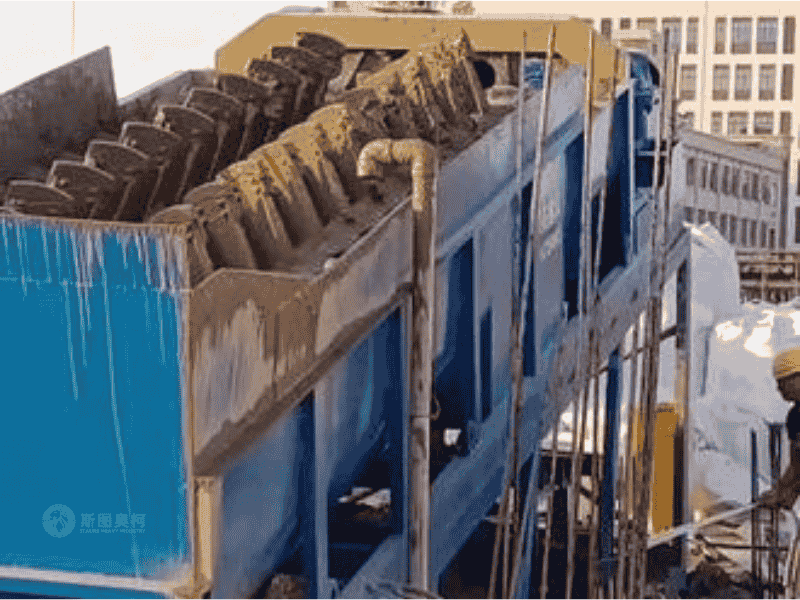




Models
Model | Capacity (TPH) | Power (kW) | Weight (kg) | Dimensions (L x W x H, mm) | Water Consumption (m³/h) |
LW-50 | 50-70 | 15 | 5,000 | 6,000 x 2,000 x 2,500 | 50 |
LW-100 | 100-120 | 22 | 7,500 | 7,500 x 2,500 x 3,000 | 80 |
LW-150 | 150-180 | 30 | 10,000 | 9,000 x 3,000 x 3,500 | 120 |
LW-200 | 200-250 | 45 | 12,500 | 10,500 x 3,500 x 4,000 | 150 |
LW-300 | 300-350 | 55 | 15,000 | 12,000 x 4,000 x 4,500 | 200 |