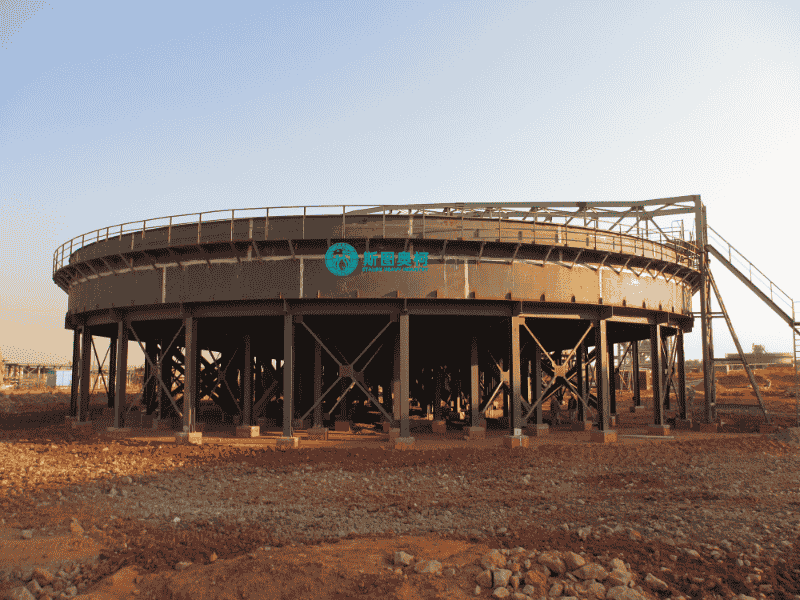
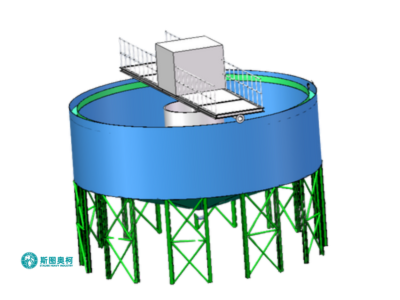
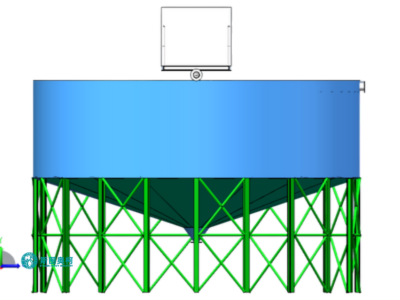
High Efficiency Thickener
Capacity: 10-1000 m³/h
Feeding Size: 0–300μm
Discharging Size: 40–70% solids
Handling Materials: Tailings dewatering, concentrate concentration, sludge dewatering, etc.
A high efficiency thickener is a advanced sedimentation device used to concentrate slurries by gravity. It features a steep-sided design, slow-turning rakes, and flocculant addition to enhance settling. Compared to conventional thickeners, it offers faster processing, higher underflow density, and smaller footprint. Ideal for mining and wastewater treatment, it ensures optimal solid-liquid separation with lower energy consumption and operational costs.
Advantages
01.
Faster Processing
Achieves rapid solid-liquid separation with enhanced settling rates, reducing retention time and increasing throughput compared to conventional thickeners.
02.
Higher Density
Produces thicker underflow with greater solids concentration, minimizing water content and improving downstream handling or disposal.
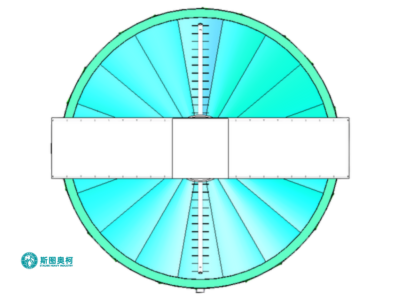
03.
Compact Design
Requires less floor space due to steep-sided structure, making it ideal for installations with limited area.
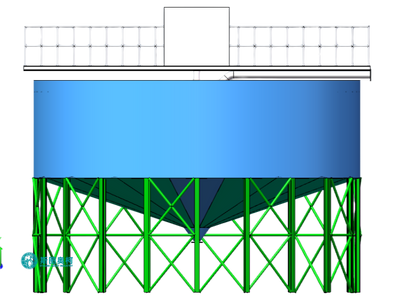
04.
Lower Costs
Reduces energy use, chemical consumption, and maintenance needs, leading to significant operational savings.
How Does A High Efficiency Thickener Work
1. Gravity Settling: Slurry enters the thickener, where solid particles gradually sink due to gravity. Larger particles settle faster, while finer ones require floculants.
2. Floculation Aid: Polymer floculants are added to bind fine particles into larger clusters (flocs), accelerating settling and improving clarity of the overflow water.
3. Rake Mechanism: Slow-moving rakes at the bottom gently push settled solids toward the discharge point, preventing compaction while ensuring smooth underflow extraction.
4. Continuous Separation: Clear water overflows from the top, while thickened slurry (underflow) is pumped out from the bottom, maintaining a steady, efficient process.
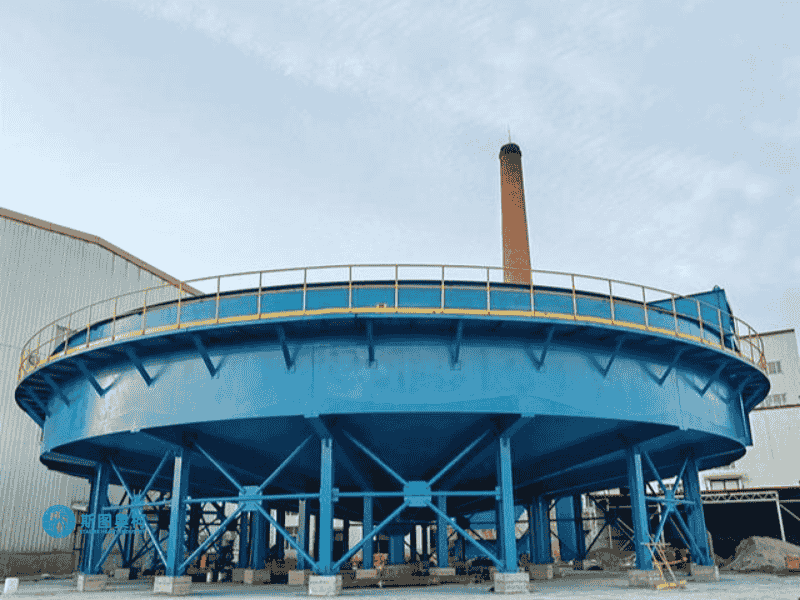

Applications
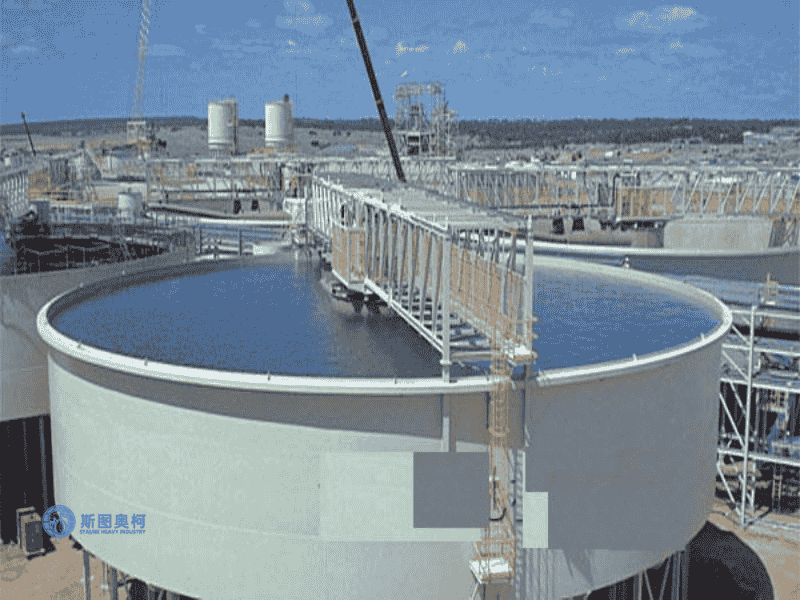
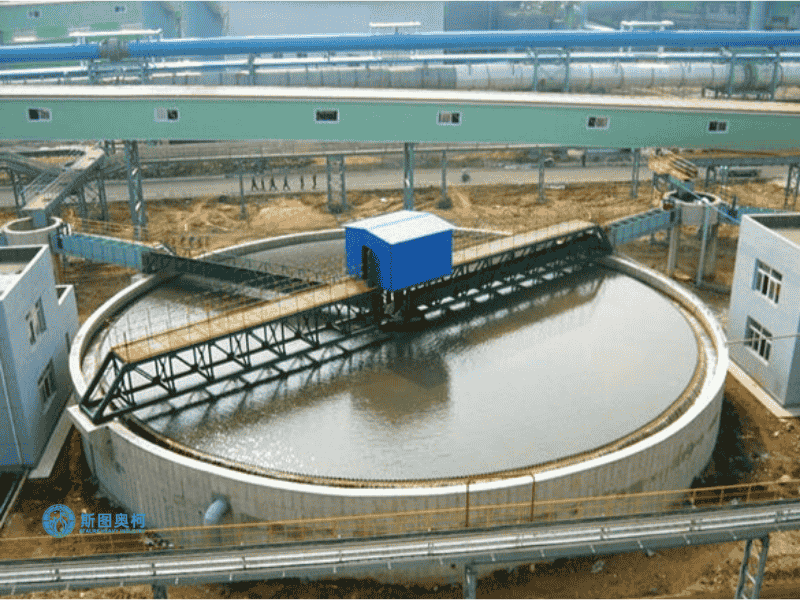
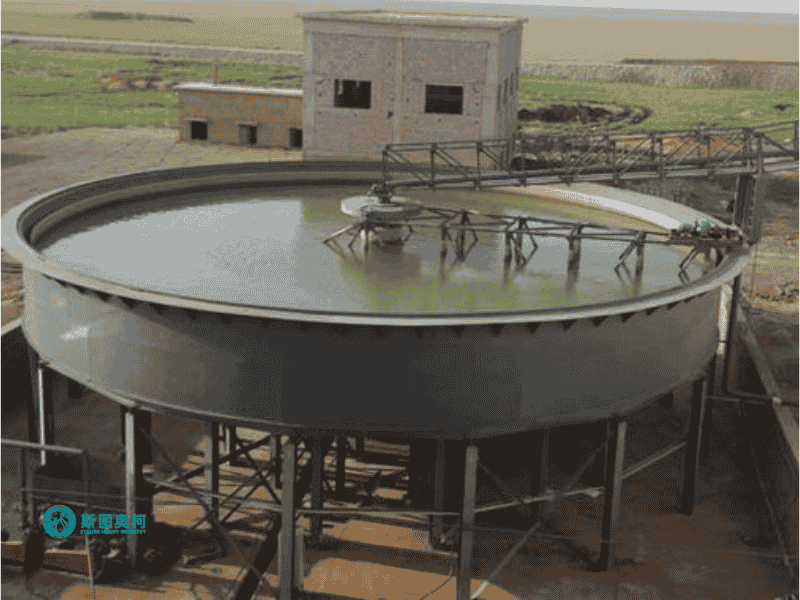
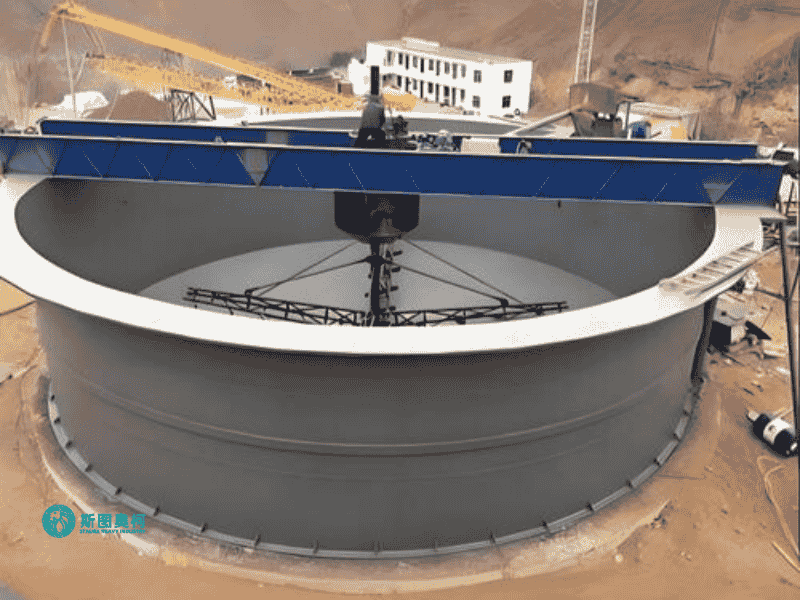




Models
Model | Diameter (m) | Processing Capacity (t/h) | Motor Power (kW) | Underflow Concentration (%) | Overflow Clarity (NTU) | Weight (kg) |
HT-6 | 6 | 50-100 | 2.2 | 50-60 | ≤200 | 5,000 |
HT-9 | 9 | 100-200 | 3.7 | 55-65 | ≤150 | 8,000 |
HT-12 | 12 | 200-400 | 5.5 | 60-70 | ≤100 | 12,000 |
HT-15 | 15 | 400-600 | 7.5 | 65-75 | ≤50 | 18,000 |
HT-18 | 18 | 600-800 | 11 | 70-80 | ≤30 | 25,000 |
HT-24 | 24 | 800-1200 | 15 | 75-85 | ≤20 | 35,000 |